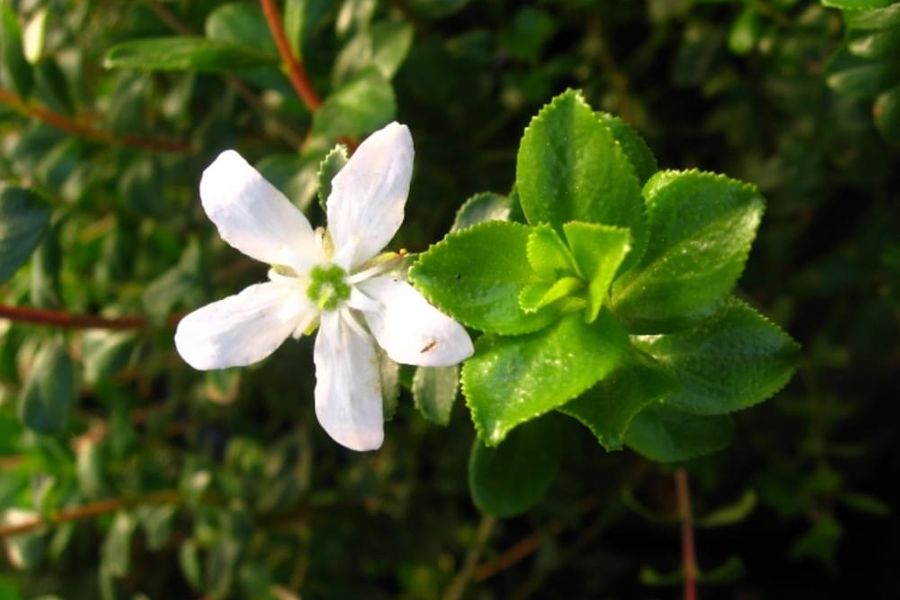
Barosma Betulina
HISTORY AND USE
The buchu is native to South Africa It is also grown in some countries in South America. We use cuttings in late summer on well-irrigated soils and very sunny.
DESCRIPTION OF THE PLANT
Traditional Remedy South Africa, the buchu is a stimulant and a diuretic, it also relieves intestinal diseases.For the Western herbal medicine, it is a diuretic agent and a valuable antiseptic unary, used in particular to cure the cystitis and d other diseases of the unary system The aroma of the buchu is strong and its taste is reminiscent of rosemary and peppermint.

CURATIVE ACTION
African Remedy
The buchu is the medicinal plant of the Hottentots of Namibia, who use it as a diuretic and stimulant It is also a carminative treatment, which helps to expel flatulence and reduces bloating abdominals.
Western First Uses
Introduced in Great Britain in 1790, the plant became an official medicine in 1821, cited in the British Pharmacopoeia as an effective treatment against cystitis, nephritis, urethritis and inflammation of the bladder.
Modern Treatment
In general, buchu is still used today to treat the same conditions as in the previous century. It is present for infections of the unary system, often proving effective in treating acute cystitis when associated with other plants, such as maize.
Gynecology
In infusion or tincture, buchu cystitis and urethritis, especially when these diseases are linked to the existence of candida albicans, responsible for vaginal candidiasis The infusion is generally more effective dyeing, especially when the infection is sudden Infused, the buchu is used in vaginal douche in case of leucorrhea (white discharge), and incidentally for vaginal inflammations The plant is a uterine stimulant that contains pulegone. Therefore, the buchu is not recommended during pregnancy.

USES
Infusion
- For the prostate, drink a cup 2 times a day.
- Tincture For chronic unic infections, take 40 drops in water 3 times a day.
- Capsule For cystitis, take one capsule of 500 mg twice a day.