Ginkgo Biloba
1. History and use
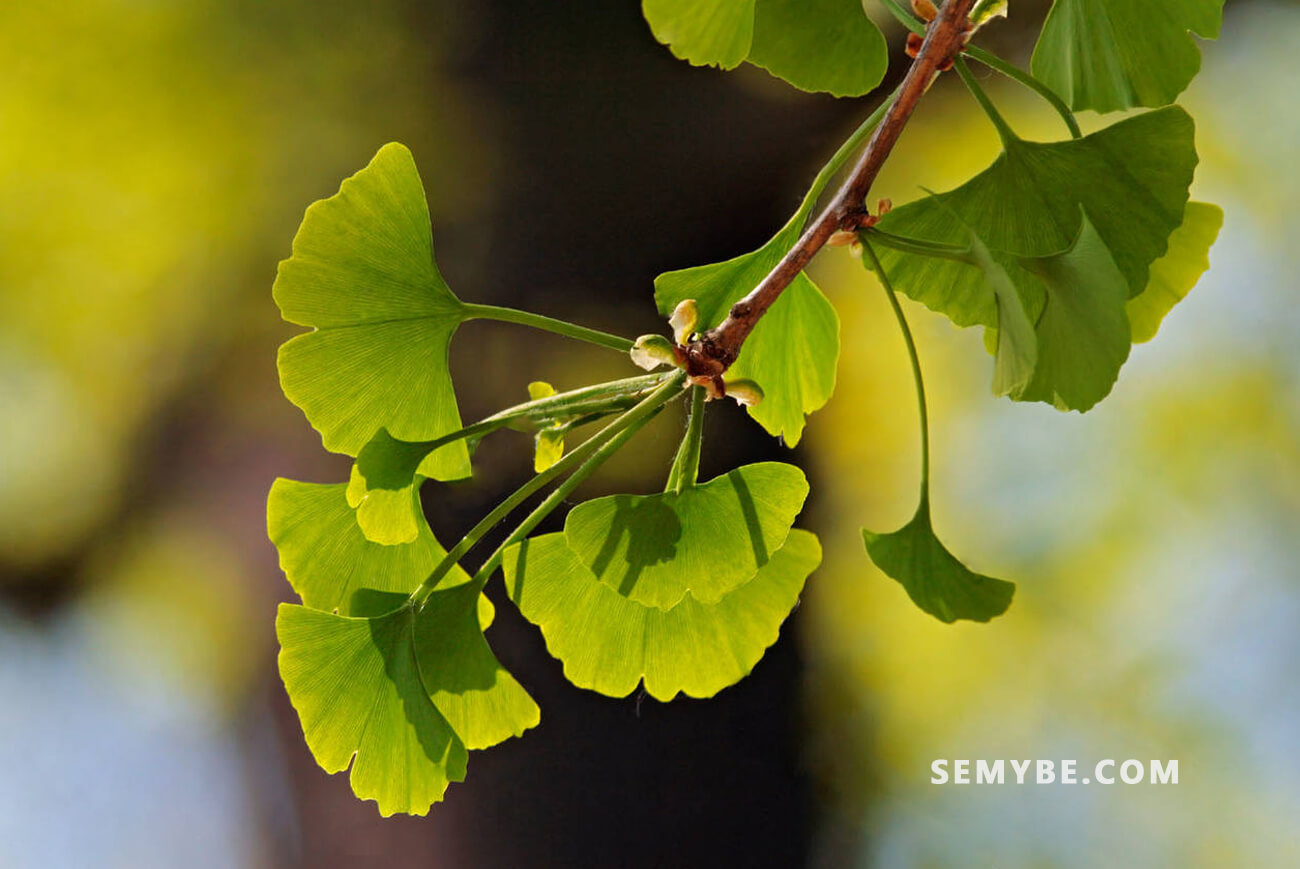
Native to Asia , ginkgo is cultivated in China , France and the United States (South Carolina). It produces yellow – green , fan – shaped leaves with radiating veins, as well as pseudo – fruits round, about 3 cm in diameter. Leaves and pseudo – fruits are harvested in autumn.
2. Description of the plan
Even if nothing suggests, since its foliage is not persistent and it does not bear any cones, the ginkgo biloba is a coniferous tree, reaching 40 m high, it adopts a very spread form and is covered with small, delicately ribbed leaves, turning from light green to golden yellow in autumn, a dioecious species with male and female trees , and only the second bears fruit (small yellow berries of about 3 cm with an edible core) which, when ripe, spread an unpleasant smell. Westerners prefer especially the leaves (fresh or dried) which concentrate the most active ingredients the Chinese also use the seeds.

3. Curative action
- Internal use
Ginkgo biloba Promotes good blood circulation: anticoagulant, anti – aggregating (prevents the formation of thromboses or clots), vasodilator (facilitates the dilation of the blood vessels). Reinforces the brain functions, mainly in case senile dementia stimulates memory, helps concentration and reasoning.
In Asia, ginkgo leaves are used in decoctions to relieve respiratory diseases such as asthma or bronchitis (expectorant and sedative effects), but also as a dewormer. The seeds are used to prepare remedies for urinary disorders.
- External use
Helps healing ulcers, bruises, burns (poultices of crushed leaves on the injured areas). Many anti – aging cosmetics (creams) use ginkgo as a base for its properties protective and restorative on the skin (antioxidant, anti – inflammatory and stimulant effects), especially in case of rosacea. In Asia , the leaves also serve as poultices to cure frostbite.
- Other therapeutic indications demonstrated
Disorders related to cerebral circulatory insufficiency: memory loss, decreased concentration, dizziness, headache , hearing loss , tinnitus, tinnitus, senile dementia, Alzheimer’s disease (in its infancy).
4. Uses
The many ginkgo medicines on the market (capsules , tablets or oral solutions) usually contain the same concentration of active ingredients, which is taken into account in clinical trials (standardized ginkgo extract titrated at 24 % flavonoids and 6 % ginkgolides bilobalides). It is recommended to take 120 to 240 mg standardized extract daily, in 2 or 3 times, with water and at the time of meals.
Hydroalcoholic extracts ( mother tinctures). Take 20 to 40 drops in water , 3 times a day.
Herbal teas and decoctions Use 20 to 40 g of fresh flowers or 2 or 3 teaspoons of dried flowers per liter of water. Drinking 1 cup 2 to 3 times a day in case of circulatory problems. The dose at 1 teaspoon per cup, the beverage becomes deworming.