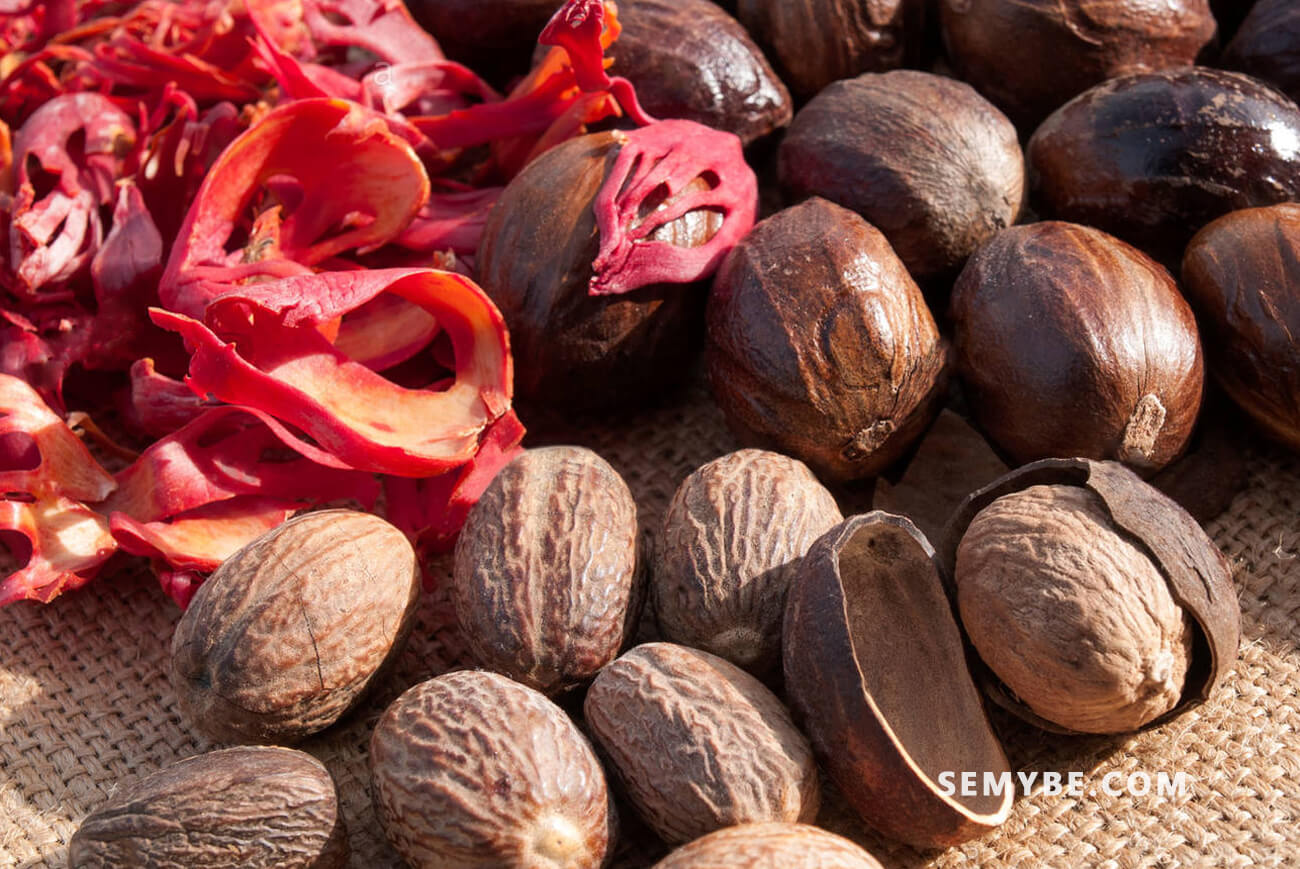
Myristica Fragrans
1. History and use
Native to the Maluku Islands, nutmeg grows in the tropics. The tree bears fruit after 8 years and can continue to produce for more than 60 years. The ripe fruits are picked, and the nuts are separated flowers to dry them.
2. Description of the plant
Both nutmeg and mace come from nutmeg and their therapeutic properties are similar. Used with caution in the West because of their toxicity, they are used to stimulate digestion and treat diseases of the digestive system. Nutmeg has long been considered an aphrodisiac, treating eczema and rheumatism.

3. Curative action
- Digestive disorders
The essential oil of nutmeg has an anesthetic and stimulating effect on the stomach and intestines. It increases appetite, reduces nausea, vomiting and diarrhea and treats gastrointestinal.
- Chinese medicine
In China, nutmeg mainly cures diarrhea, relieves abdominal pain and bloating.
- Aphrodisiac
In India, this plant has long been known to increase sexual vigor.
- External Applications
Fixed oil-based ointments (nutmeg butter) treat rheumatism. They have an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulate blood flow in the affected area. In India, we make a paste with nutmeg and it is applied on the areas affected by eczema and ringworm.
- Toxicity
In small doses, nutmeg and mace are safe (in medical or culinary use). But, in excessive doses, they are hallucinogenic and toxic Consuming two whole nuts can be fatal. Mynsticin is the substance responsible for toxicity and hallucinogenic effects, and safrol isolates are carcinogenic in high doses.
4. Uses
Nutmeg crushed, To cure tablespoons with a little water, make a paste and apply eczema, mix 2. The kernel of the seed (nutmeg) is used for its stimulating effect against intestinal disorders and rheumatism. In Chinese, nutmeg is called “rou dou kou”.